Eye Disorders
Myopia Dry EyesGlaucoma
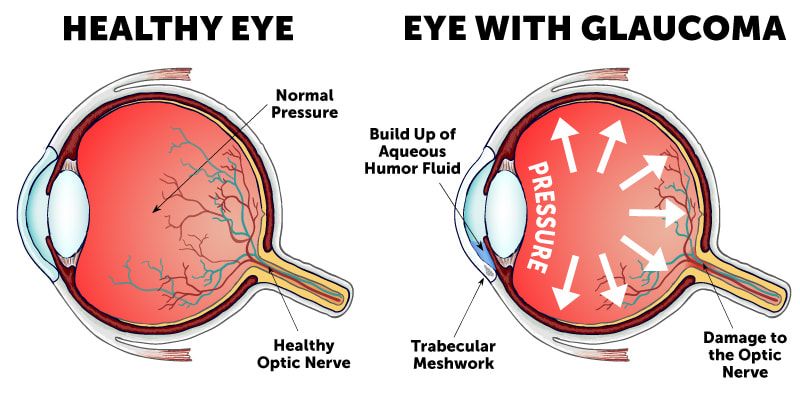
Glaucoma is a term for a group of eye disorders which result in damage to the optic nerve. This is most often due to increased pressure in the eye. The disorders can be roughly divided into two main categories: "open-angle" and "closed-angle" (or "angle closure") glaucoma. Open-angle chronic glaucoma is painless, tends to develop slowly over time and often has no symptoms until the disease has progressed significantly. Closed-angle glaucoma, however, is characterized by sudden eye pain, redness, nausea and vomiting, and other symptoms resulting from a sudden spike in intraocular pressure. Glaucoma can permanently damage vision in the affected eye(s), first by decreasing peripheral vision (reducing the visual field), and then potentially leading to blindness.
Glaucoma has been called the "silent thief of sight" because the loss of vision often occurs gradually over a long period of time, and symptoms only occur when the disease is quite advanced. Worldwide, glaucoma is the second-leading cause of blindness after cataracts. It is also the leading cause of blindness among African Americans.

